資料(liao)下載(zai)
Data download 熱門搜(sou)索:
Universal TA質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
Rapid TA質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
魚糜彈性儀
質(zhì)構(gòu)儀探(tan)頭
凝膠強度(du)測定儀
肌肉嫩(nen)度儀
Rapid TA+質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
iDeal TA物性測試儀(yi)
化工物性(xing)分析儀(yi)
納米粒子高效(xiao)自動(dong)收集裝置(zhi)
RTA-SCP土壤微型(xing)貫入儀
通針性測試(shi)儀
RTA-SA土壤粘附力測(ce)定儀
TBUTA-23質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
茶樹新(xin)梢嫩度(du)測定儀
微針(zhen)強度(du)測定儀(yi)
熱門搜(sou)索:
Universal TA質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
Rapid TA質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
魚糜彈性儀
質(zhì)構(gòu)儀探(tan)頭
凝膠強度(du)測定儀
肌肉嫩(nen)度儀
Rapid TA+質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
iDeal TA物性測試儀(yi)
化工物性(xing)分析儀(yi)
納米粒子高效(xiao)自動(dong)收集裝置(zhi)
RTA-SCP土壤微型(xing)貫入儀
通針性測試(shi)儀
RTA-SA土壤粘附力測(ce)定儀
TBUTA-23質(zhì)構(gòu)儀
茶樹新(xin)梢嫩度(du)測定儀
微針(zhen)強度(du)測定儀(yi)
 發(fā)布時(shi)間:2025/10/05
發(fā)布時(shi)間:2025/10/05 點擊次數(shù)(shu):1432
點擊次數(shù)(shu):1432
ABSTRACT
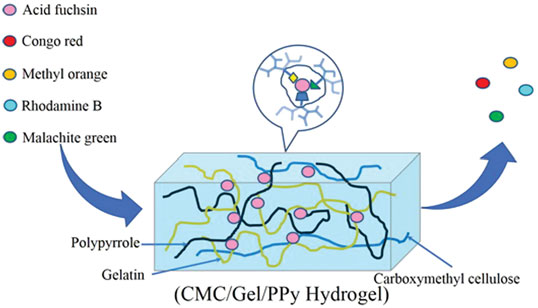
The dispersion and macroization of nanomaterials have great potential in the development of?high-efficiency adsorbents. To address organic dye pollution, two inexpensive and renewable biological?resources, gelatin (Gel) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), were crosslinked by nanostructured?polypyrrole (PPy) to achieve a novel PPy-hydrogel. The morphology and composition of the?CMC/Gel/PPy hydrogels were characterized. The result shows that the CMC/Gel solution can provide?an excellent condition for the dispersion of polypyrrole (PPy). Based on the combination of?PPy and the biomass matrix, specific adsorption sites can be formed by the synergistic effect of?the functional groups derived from CMC, Gel and PPy. The CMC/Gel/PPy hydrogel has an exclusive?adsorption of acid fuchsin (AF). Furthermore, the adsorption process of AF on the CMC/Gel/PPy?hydrogel was investigated, and influencing factors, such as adsorbent dosage, temperature, initial?dye concentration and adsorbent recyclability, were discussed in detail. Under optimal conditions,?the CMC/Gel/PPy hydrogel can reach an adsorption equilibrium within 50minutes in a 60mg/L AF?solution at 24 C, and the AF removal efficiency was approximately 94%. It was also observed that?the AF removal efficiencies of CMC/Gel/PPy remained almost unchanged after at least seven consecutive?adsorption–desorption cycles.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT